By: Team W14-3 Since: September 2018 Licence: MIT
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Quick Start
- 3. Features
- 3.1. Add appointment for patient:
addappt - 3.2. Add patient’s dietary needs:
adddiet - 3.3. Add patient medication:
addmeds - 3.4. Add to patient’s medical history:
addmh - 3.5. Check in a returning patient:
checkin - 3.6. Check out a patient:
checkout - 3.7. View help :
help - 3.8. Register a new patient to the system:
register - 3.9. Sort user view :
sort - 3.10. Select patient:
select - 3.11. View patient’s information:
view - 3.12. View all appointments for a patient:
view appt - 3.13. View patient’s dietary requirements:
view diets - 3.14. View patient medication:
view meds - 3.15. View patient visitors:
view visitors - 3.16. View patient’s medical history:
view mh - 3.17. View patient’s visitors:
viewvisitors - 3.18. Sign in patient’s visitors:
visitorin - 3.19. Sign out patient’s visitors:
visitorout - 3.20. Saving the data
- 3.21. Encrypting data files
[coming in v2.0]
- 3.1. Add appointment for patient:
- 4. FAQ
- 5. Command Summary
1. Introduction
HealthBase is for hospital administrators, doctors, nurses, and pharmacists who prefer to use a desktop app to manage patients and their associated data. More importantly, HealthBase is optimized for those who prefer to work with a Command Line Interface (CLI) while still having the benefits of a Graphical User Interface (GUI). If you can type fast, HealthBase can get your hospital management tasks done faster than traditional GUI apps.
2. Quick Start
-
Ensure that your computer has Java version
9or later installed. -
Download the latest release of our application,
healthbase.jarhere. -
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your HealthBase.
-
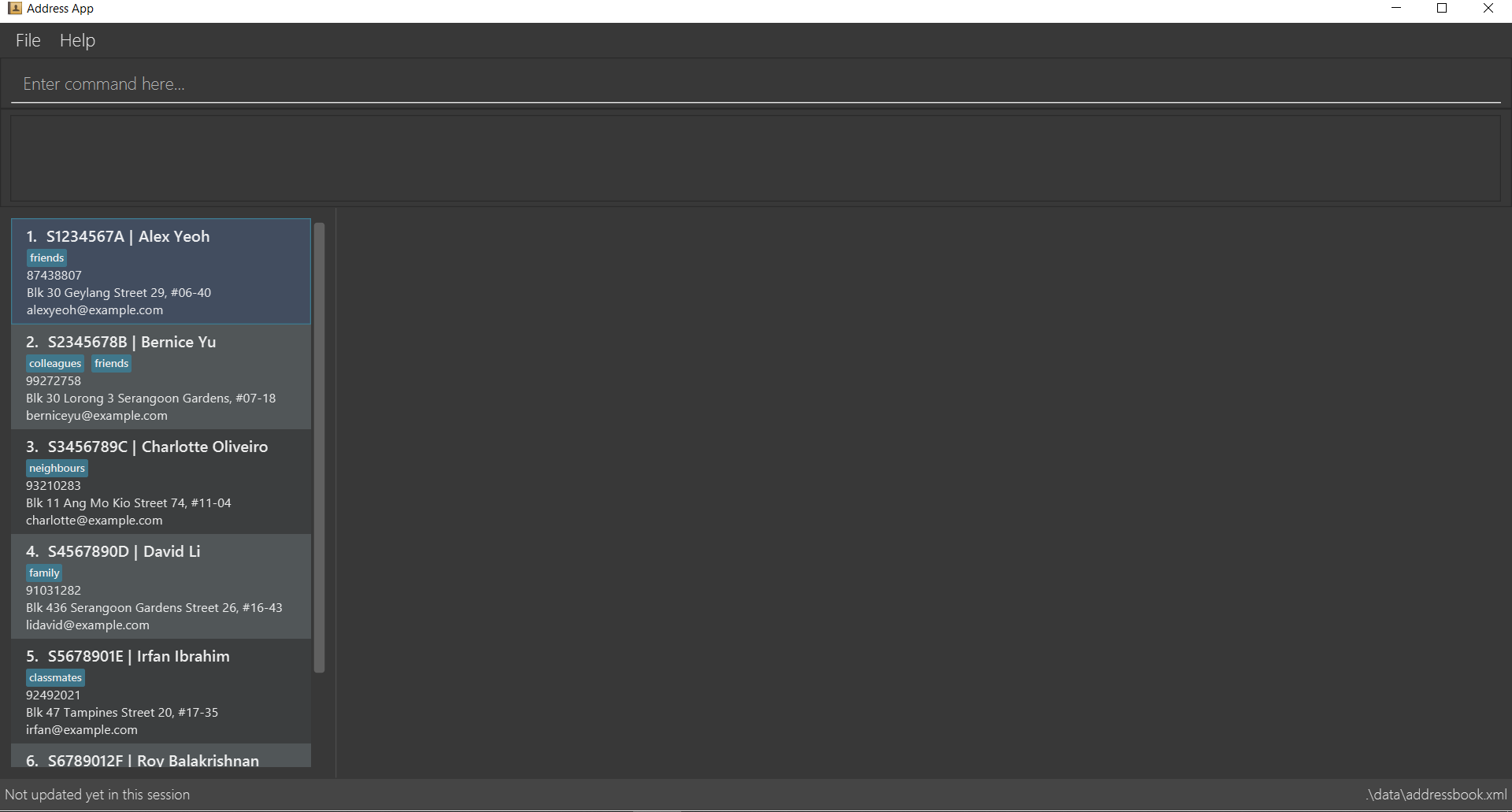
Double-click the file to start the app. The Graphical User Interface (GUI) should appear in a few seconds.
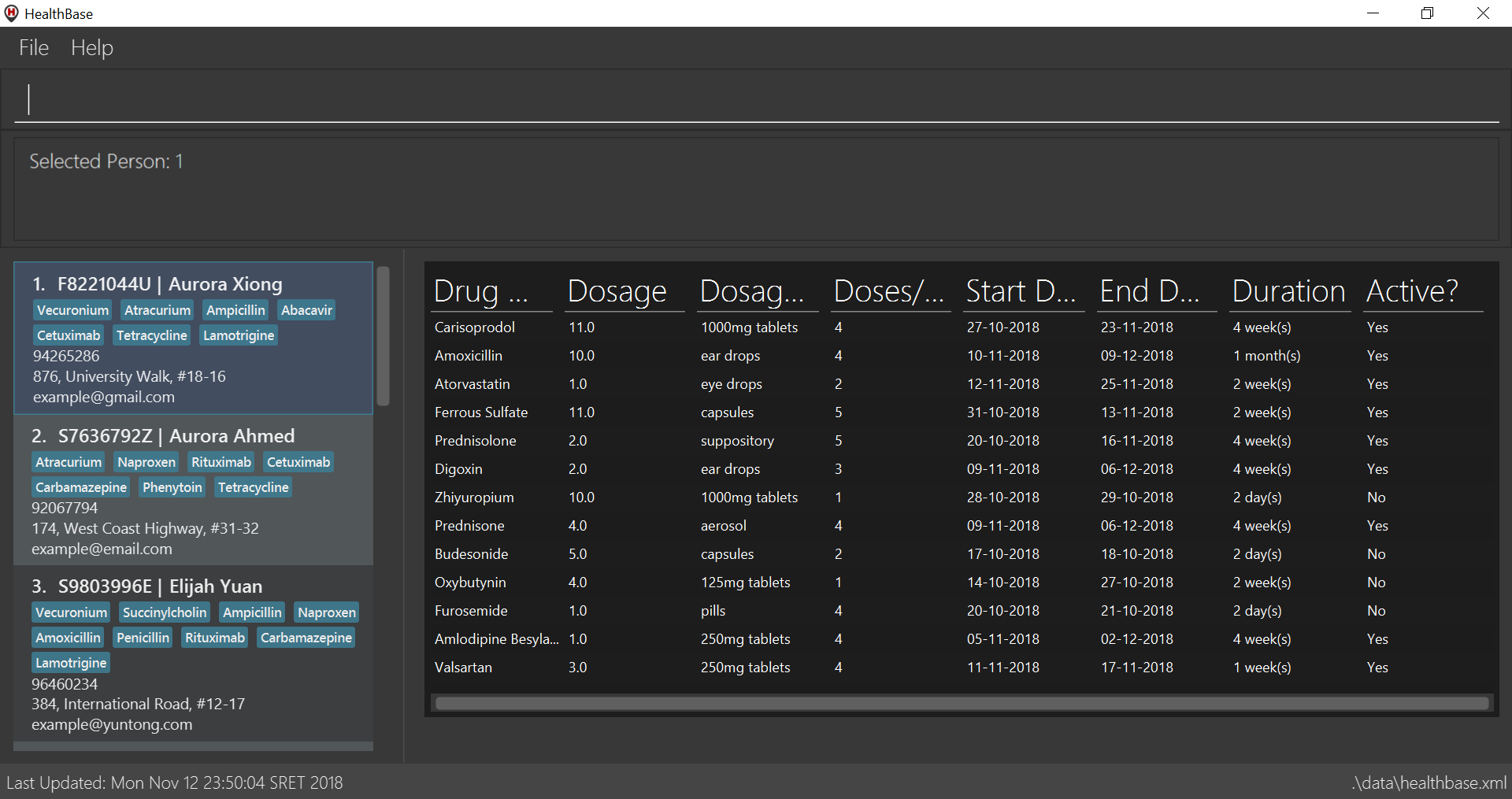 Figure 1. The GUI of HealthBase
Figure 1. The GUI of HealthBase -
Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it.
e.g. typinghelpand pressing Enter will open the help window. (The command box is shown in Fig. 1 above; it is the gray box with the words "Enter your commands here…" inside.)
Some example commands you can try:
-
exit: exits the app -
select 1: selects the first patient (Alex Yeoh in the image above) in the list of patients.
Refer to Section 3, “Features” for the details of each command.
3. Features
Command Format
-
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters to be supplied by the user e.g. inadd n/NAME,NAMEis a parameter which can be used asadd n/John Doe. -
Items in square brackets are optional e.g
n/NAME [da/DRUG ALLERGY]can be used asda/aspirin da/insulinor asn/John Doe. -
Items with
… after them can be used multiple times including zero times e.g.[da/DRUG ALLERGY]…can be used asda/aspirin,da/aspirin da/insulinetc. -
Parameters can be in any order e.g. if the command specifies
n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER,p/PHONE_NUMBER n/NAMEis also acceptable.
| Features are sorted by their command word in lexicographical order. |
3.1. Add appointment for patient: addappt
Add a scheduled appointment for a patient.
Format: addappt ic/NRIC type/TYPE pn/PROCEDURE_NAME dt/DD-MM-YYYY HH:MM doc/DOCTOR-IN-CHARGE
The only valid types are PROP (PROPAEDEUTIC), DIAG (DIAGNOSTIC), THP (THERAPEUTIC), SRG (SURGICAL).
Other inputs are not allowed.
|
| It is useful to note that HealthBase does not permit appointments of duplicate date and time for any one patient. This is to prevent appointment clashes. |
The HealthBase System assumes that there are 31 days for all months. For the inputs of the dates 31 and 29 (for February), it is the onus of the user to ensure that
the input month has 31 days (for months except February) and 29 days for February in a leap year.
|
Example(s):
-
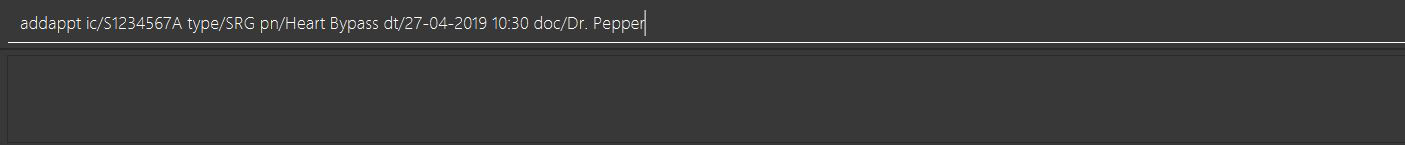
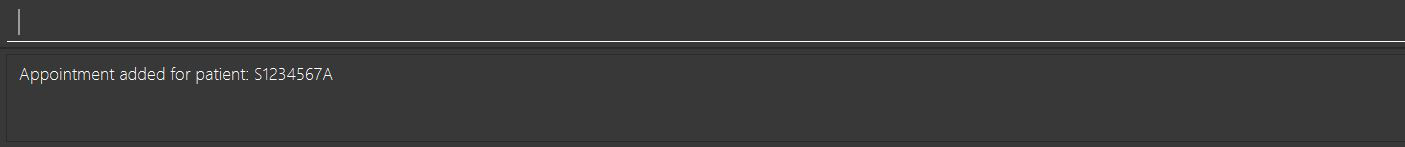
addappt ic/S1234567A type/SRG pn/Heart Bypass dt/27-04-2019 10:30 doc/Dr. Pepper
-
Type the example command into the input box as shown in the figure below and hit the Enter key:
-
The resulting output will be as shown in the figure below:
3.2. Add patient’s dietary needs: adddiet
Add a patient’s dietary requirements into the system.
Format: adddiet ic/NRIC alg/ALLERGY1 alg/ALLERGY2 cr/CULTURAL_REQUIREMENT pd/PHYSICAL_DIFFICULTY
There are three types of dietary requirements, which can be added to a patient with their own prefixes:
Type of dietary requirement |
Prefix |
Usage Example |
Allergy |
|
|
Cultural Requirement |
|
|
Physical Difficulty |
|
|
Example(s):
-
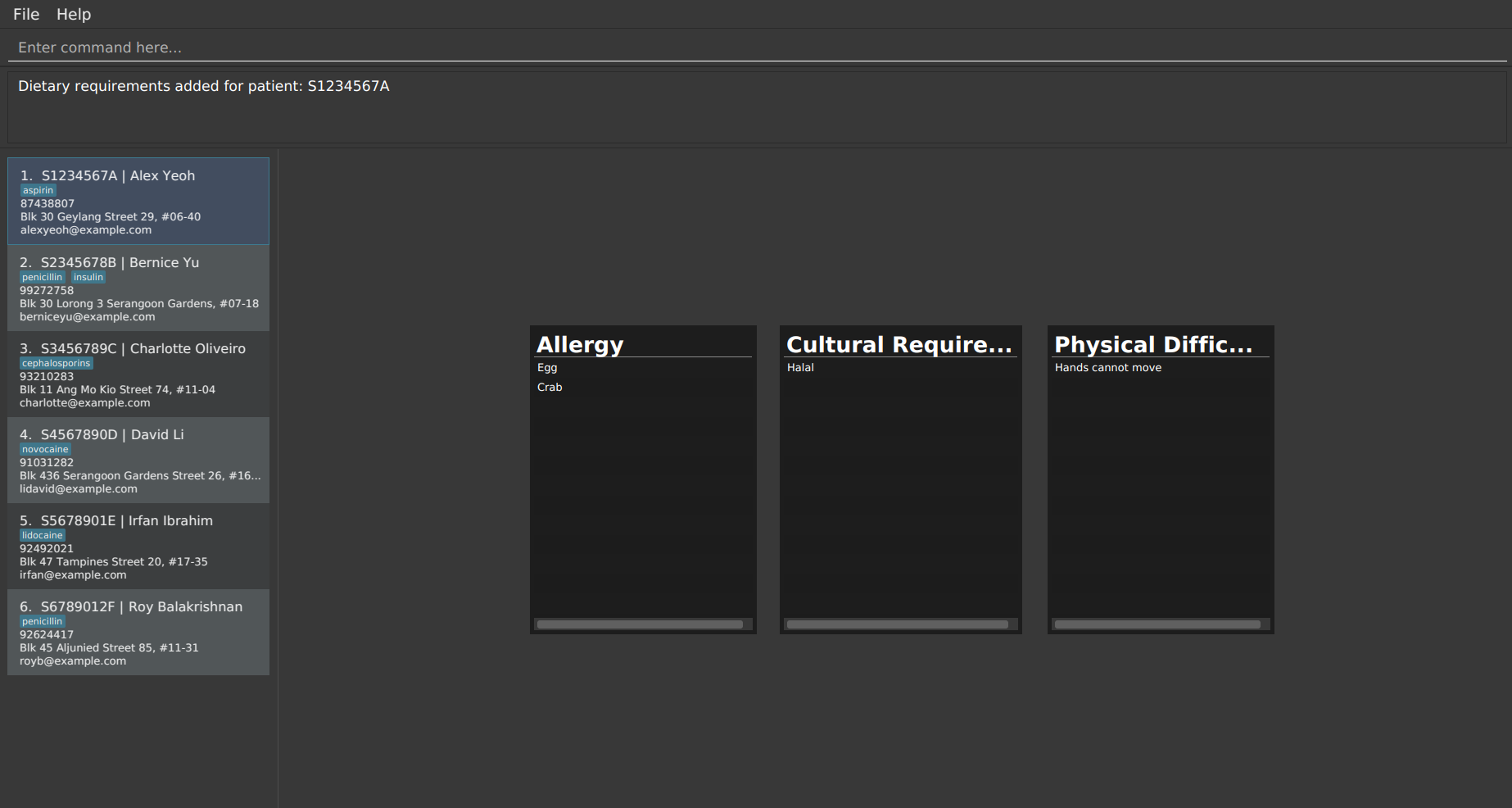
adddiet ic/S1234567A alg/Egg alg/Crab cr/Halal pd/Hands cannot move -
adddiet ic/S1234567A cr/Vegetarian
Result of executing the first example command above:
3.3. Add patient medication: addmeds
Add to a patient’s medication history.
Format: addmeds ic/NRIC d/DRUG_NAME q/QUANTITY_PER_DOSE u/DOSAGE_UNIT n/DOSES_PER_DAY t/DURATION_IN_DAYS
Example(s):
-
addmeds ic/S1234567A d/Paracetamol q/2 u/tablets n/4 t/14
3.4. Add to patient’s medical history: addmh
Add a non-blank diagnosis entry with the name of the doctor-in-charge to an existing patient’s medical history. The patient must be registered within the system and the doctor’s name should contain his title which is followed by his full name. For all words in the doctor’s name, the starting letter must be capitalised.
Format: addmh ic/NRIC mh/DIAGNOSIS doc/DOCTOR-IN-CHARGE
Example(s):
-
addmh ic/S1234567A mh/Patient shows symptoms of flu. Prescribed 2 weeks of panadol, advised patient to rest and rehydrate. doc/Dr. Zhang De -
addmh ic/T9876543Z mh/Patient appears to have chronic cough. Referred to specialist. doc/Dr.Timothy
To try out the addmh command:
-
Type out a valid
addmhcommand which follows the stated format into the command box. Such an example can be seen in the figure below. -
Submit the input into HealthBase by pressing Enter. The result display panel will show a successful
addmhcommand message, and should show the further figure below.
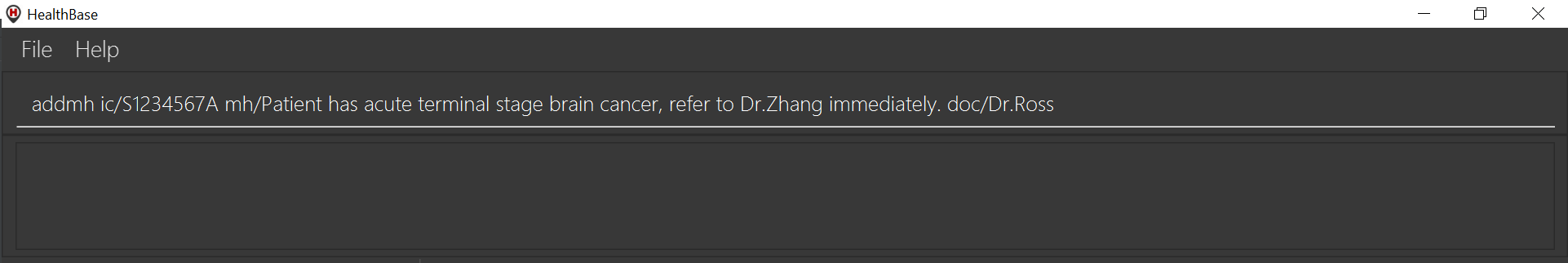
addmh command.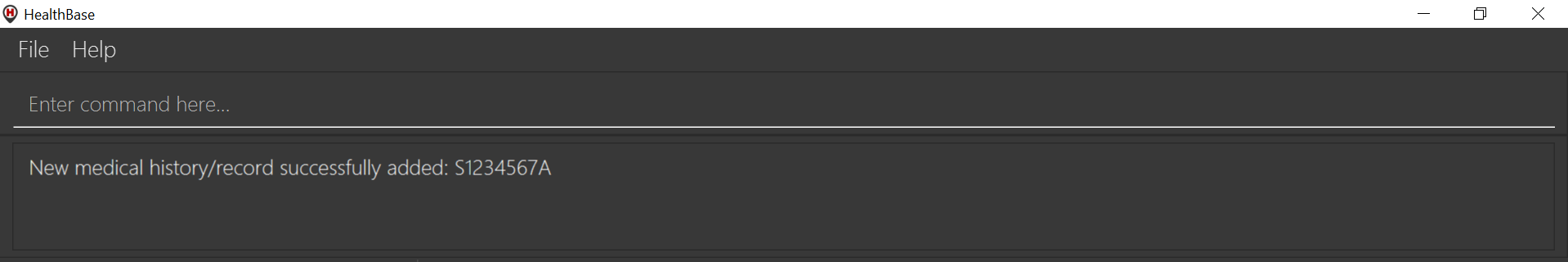
addmh command.|
If you want to view the newly added diagnoses to a particular patient, simply enter |
3.5. Check in a returning patient: checkin
Check in a returning patient back to the HealthBase system, and retrieve his/her information from backend and display
them in the left panel of the application window. The patient being checked in must have been previously registered
to the system and were checked out of the system sometime before by using the checkout command.
Format: checkin ic/NRIC
Example(s):
-
checkin ic/S1234567A
Note that the patient withNRIC S1234567Amust have been previously registered to the system and were checked out of the system sometime before by using thecheckoutcommand.
3.6. Check out a patient: checkout
Check out a patient from the HealthBase system, while still keeping the information of the patient at the backend. Upon checking out a particular patient, this patient will not be displayed in the left panel of the application.
Format: checkout ic/NRIC
Example(s):
-
checkout ic/S1234567A
3.8. Register a new patient to the system: register
Register a new patient together with necessary information into the system.
Format: register ic/NRIC n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS da/DRUG_ALLERGIES
| If the patient is already registered, the command will not be allowed. |
The prefix da/ must be separated from the last input by a whitespace
|
Example(s):
-
register ic/S1234567A n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/311, Clementi Ave 2, #02-25 da/aspirin da/insulin
-
Type the example command into the input box as shown in the figure below and hit the Enter key:
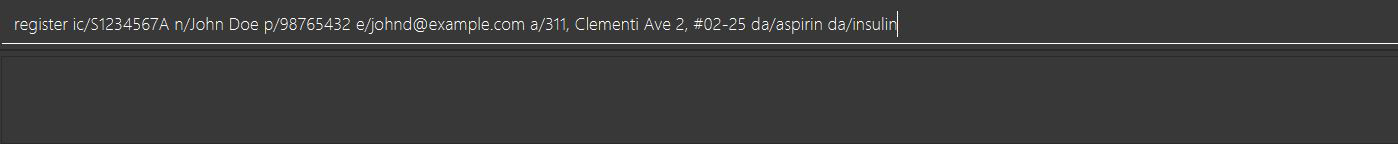
-
The resulting output will be as shown in the figure below:

3.9. Sort user view : sort
Sort the current view, if it is sortable.
Format: sort SORT_TYPE SORT_ORDER
SORT_TYPE refers to the order in which the sorting should be done (ascending, descending).
It can be either 'a' for ascending, or 'd' for descending.
SORT_ORDER refers to the order in which the sorting should be done.
How this affects the sorting exactly depends on each view, and will be explained in greater detail below.
View Name |
Sortable? |
What |
Default |
No |
- |
Apppointment |
Yes |
The columns of the table in the view, one-indexed. |
Diet |
No |
- |
Medication |
Yes |
The columns of the table in the view, one-indexed. |
Medical History |
Yes |
The columns of the table in the view, one-indexed. |
Example(s):
-
sort a 123where the current view is Medication-
Sorts the table in the medication view by the first column (Drug Name). Any entries with the same drug name will be further sorted by the second column (Dosage), with any entries with the same drug name and dosage being further sorted by the third column (Dosage Unit).
-
-
sort a 1where the current view is the default view (blank view).-
Does nothing (the current view is not sortable).
-
3.10. Select patient: select
Select a patient through pure command-line functionality. The alternative is to click on the patient’s card.
Format: select INDEX
where INDEX refers to the index of the patient’s card (listed in the card)

Example(s):
-
select 1
3.11. View patient’s information: view
View a selected patient’s information in the panel on the right. Exactly what information is displayed depends on the choice of view.
Selected here refers to the use of the select command. To view the information of a given patient, he must first be select ed.
|
Format: view VIEW_NAME
Current choices for views include:
-
default (This is the default blank view, which is displayed when the application is started)
-
appt (Appointment view, contains patient’s appointments)
-
diets (Diet view, contains patient’s dietary requirements)
-
meds (Medication view, contains information about the patient’s medications)
-
mh (Medical history view, contains patient’s previous medical diagnoses)
-
visitors (Visitor list view, contains patient’s visitors' names)
This command switches the user’s view (right panel of the UI, indicated in the figure directly below) to a chosen view.

Example(s):
-
view default
-
view appt
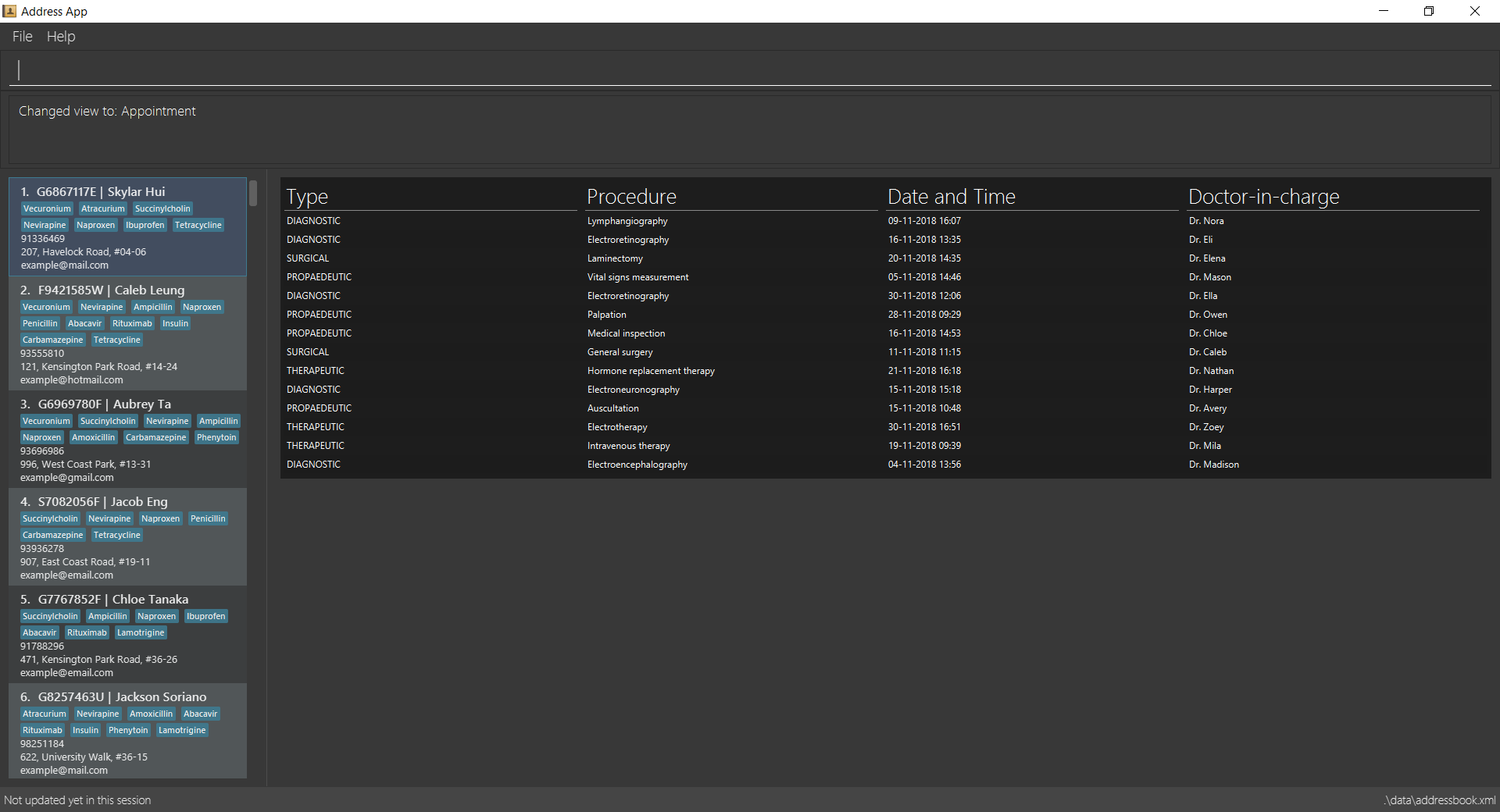
-
view diets
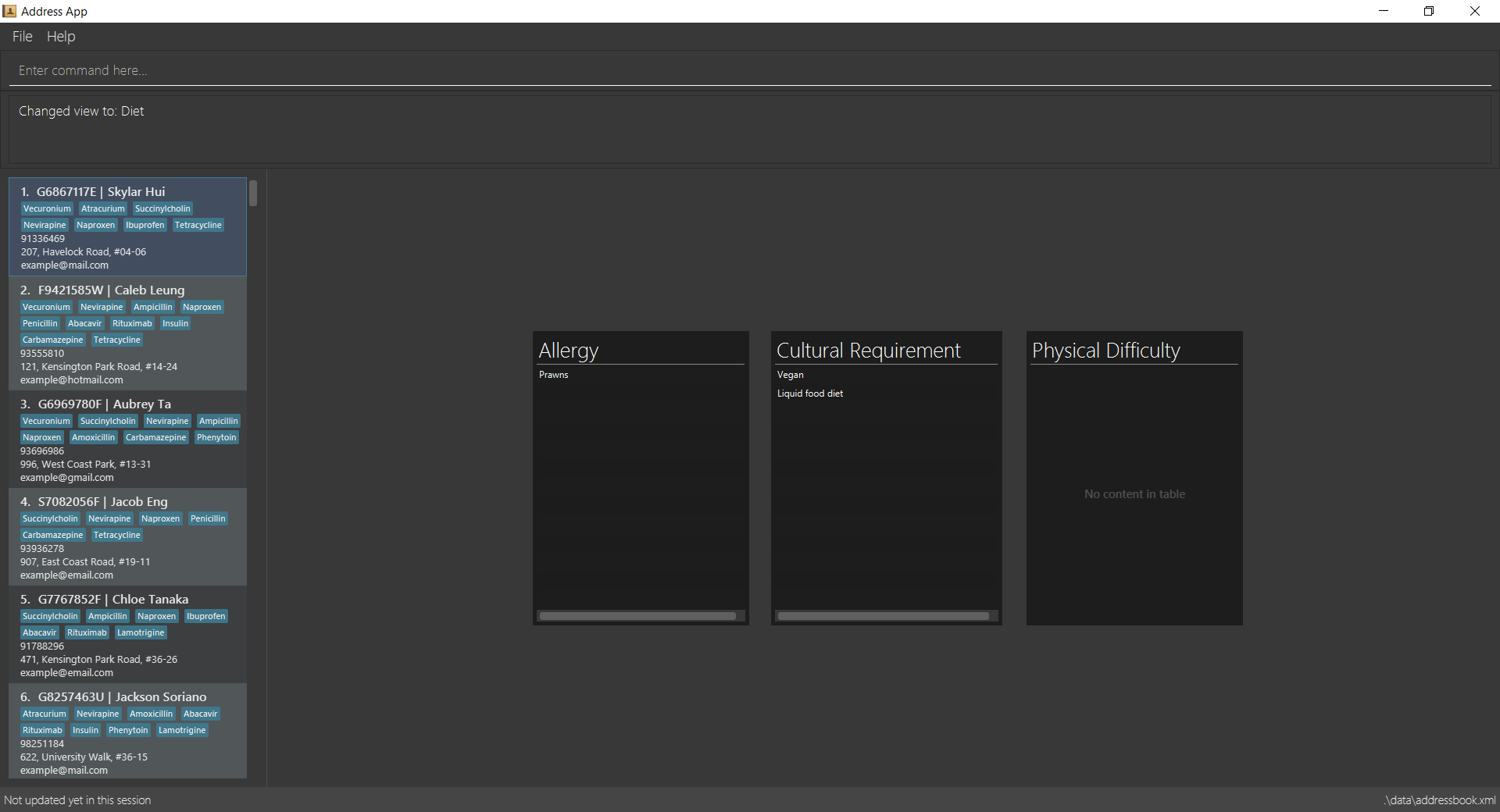
-
view meds
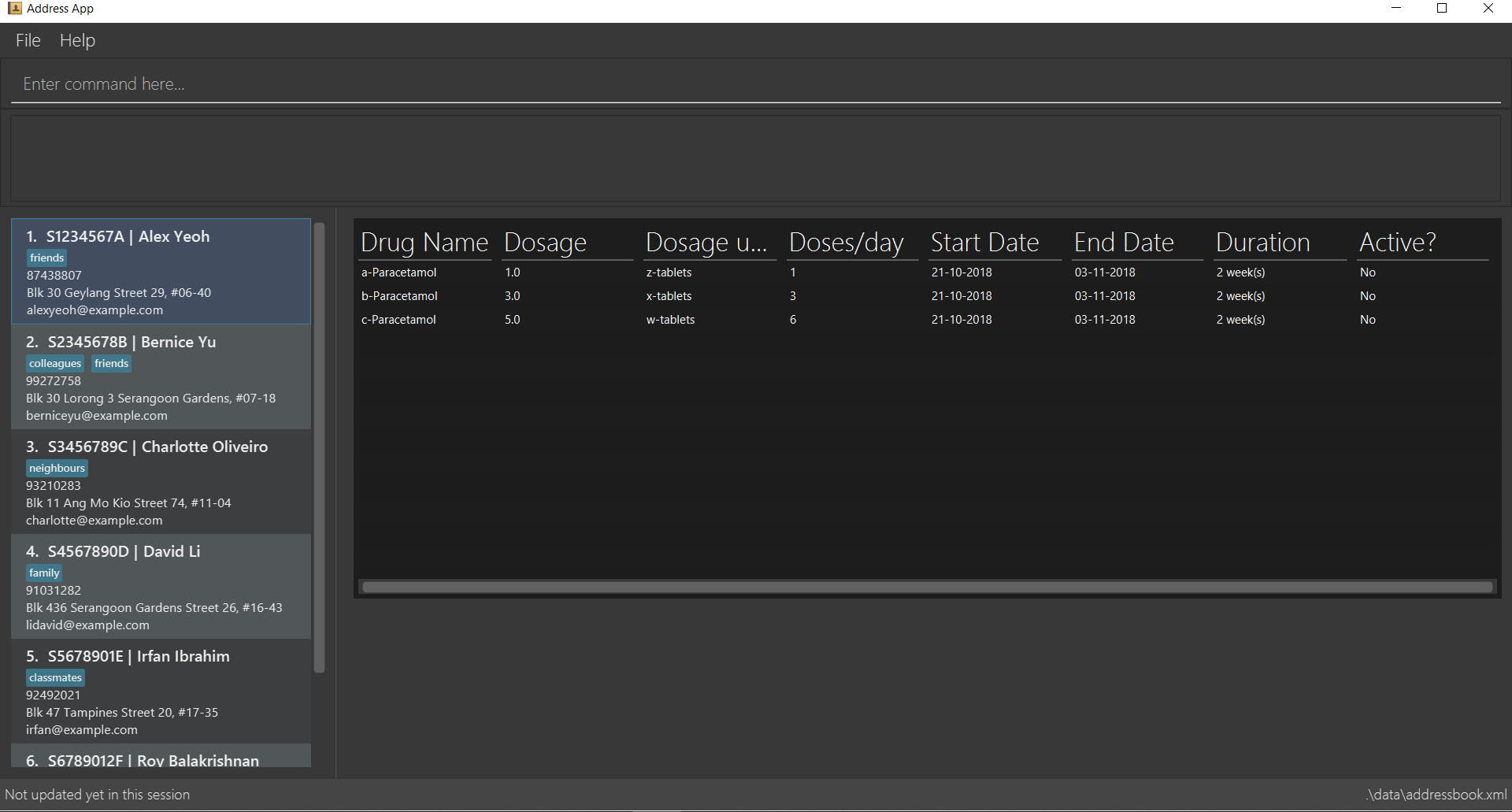
-
view mh
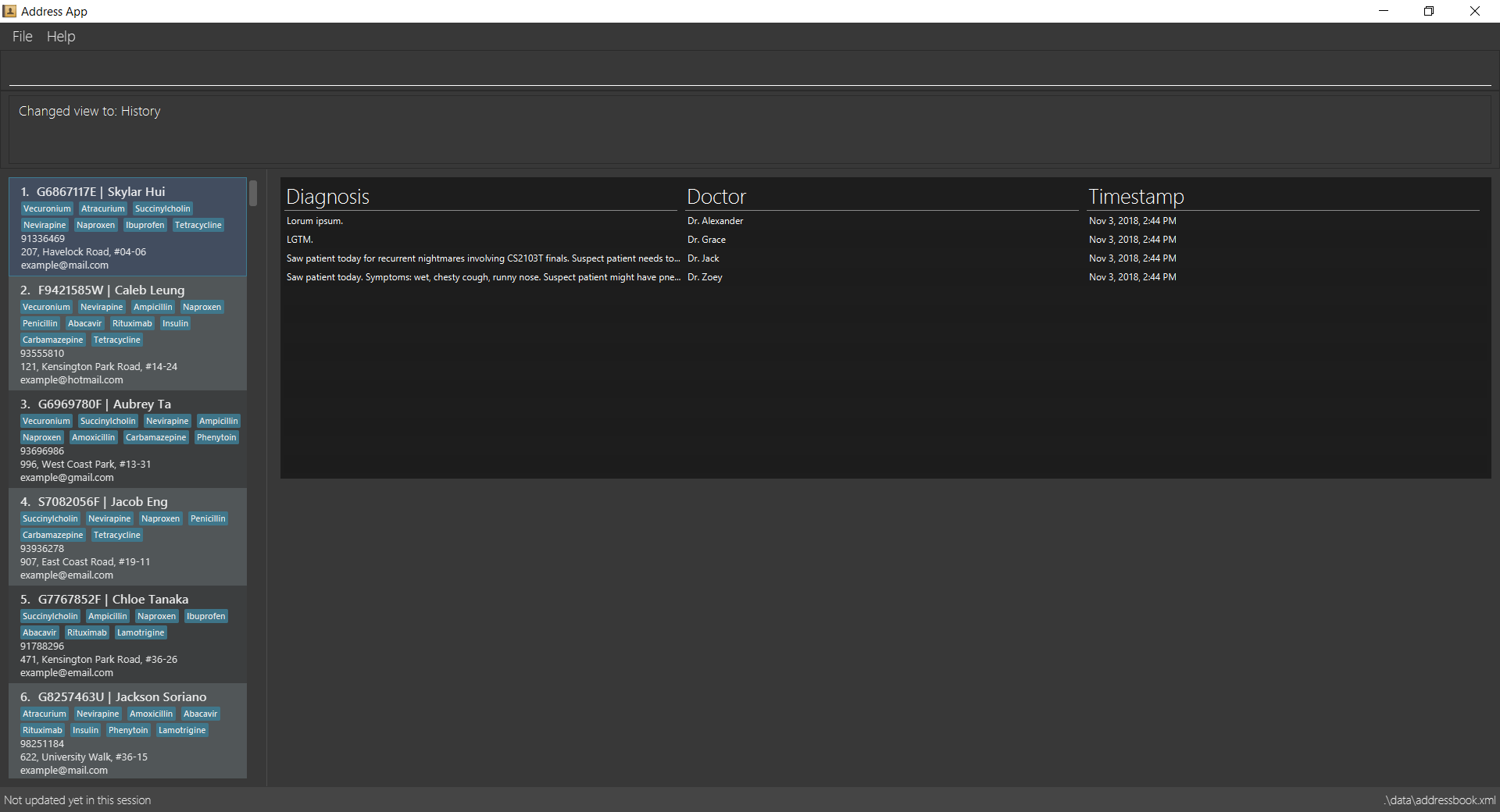
-
view visitors
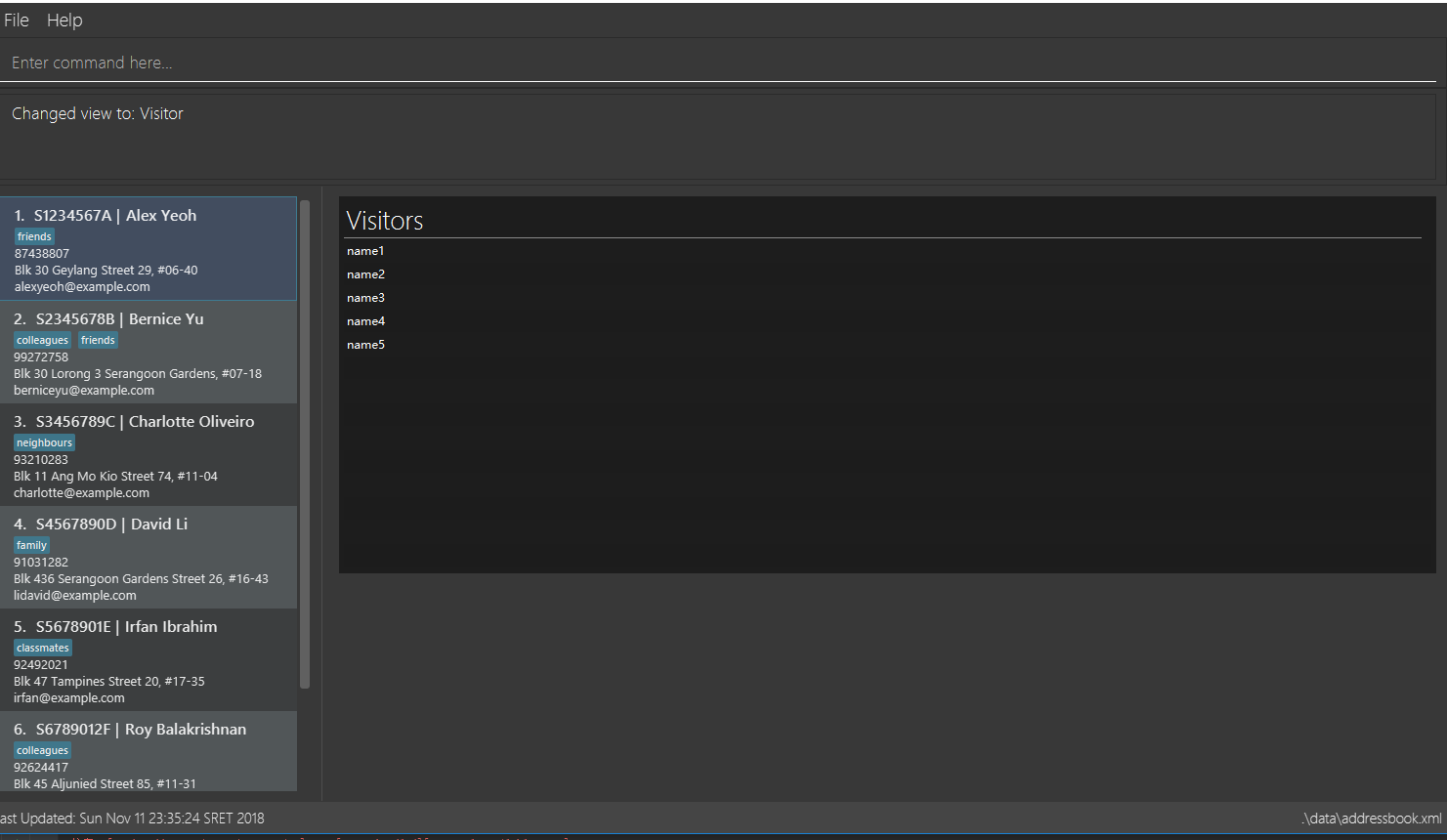
3.12. View all appointments for a patient: view appt
See entry on the view command.
3.13. View patient’s dietary requirements: view diets
View an existing patient’s recorded dietary requirements.
See entry on the view command.
3.14. View patient medication: view meds
See entry on the view command.
3.15. View patient visitors: view visitors
See entry on the view command.
3.16. View patient’s medical history: view mh
View an existing patient’s recorded medical history.
See entry on the view command.
Example(s):
-
view mh ic/S1234567A
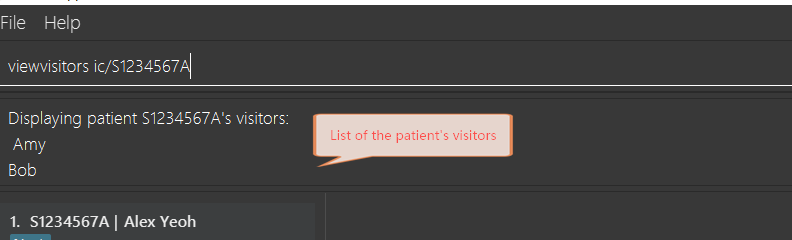
3.17. View patient’s visitors: viewvisitors
View a particular patient’s visitors.
Format: viewvisitors ic/PATIENT_NRIC
Example:
-
viewvisitors ic/S1234567A
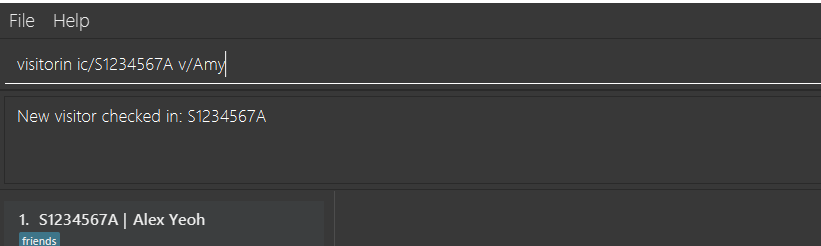
3.18. Sign in patient’s visitors: visitorin
Sign in a visitor for a patient.
Format: visitorin ic/PATIENT_NRIC v/VISITOR_NAME
Example:
-
visitorin ic/S1234567A v/Amy
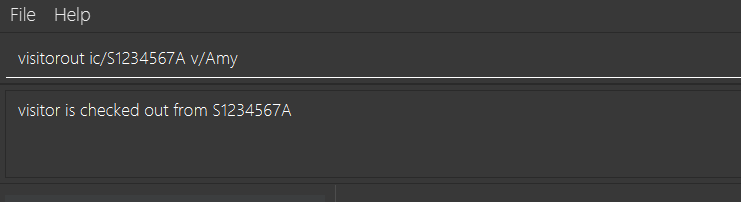
3.19. Sign out patient’s visitors: visitorout
Sign out a visitor for a patient.
Format: visitorout ic/PATIENT_NRIC v/VISITOR_NAME
Example:
-
visitorout ic/S1234567A v/Amy
3.20. Saving the data
Patient data is saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data.
There is no need to save manually.
3.21. Encrypting data files [coming in v2.0]
{explain how the user can enable/disable data encryption}
4. FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another computer?
A: Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous app folder.
5. Command Summary
Each command below will be summarised in the following format:
Command name
-
Command format
-
Example(s) of use
addappt
-
addappt ic/NRIC type/TYPE pn/PROCEDURE_NAME dt/DD-MM-YYYY HHMM doc/DOCTOR-IN-CHARGE -
addappt ic/S1234567A type/SRG pn/Heart Bypass dt/27-04-2019 1030 doc/Dr. Pepper
adddiet
-
adddiet ic/NRIC alg/ALLERGY1 alg/ALLERGY2 cr/CULTURAL_REQUIREMENT pd/PHYSICAL_DIFFICULTY -
adddiet ic/S1234567A alg/Egg alg/Crab cr/Halal pd/Hands cannot move
addmeds
-
addmeds ic/NRIC d/DRUG_NAME q/QUANTITY_PER_DOSE u/DOSAGE_UNIT n/DOSES_PER_DAY t/DURATION_IN_DAYS -
addmeds ic/S1234567A d/Paracetamol q/2 u/tablets n/4 t/14
addmh
-
addmh ic/NRIC mh/DIAGNOSIS doc/DOCTOR-IN-CHARGE -
addmh ic/S1234567A mh/Patient shows symptoms of flu. Prescribed 2 weeks of panadol, advised patient to rest and rehydrate. doc/Dr.Zhang De Chou
checkin
-
checkin ic/NRIC -
checkin ic/S1234567A
checkout
-
checkout ic/NRIC -
checkout ic/S1234567A
register
-
register ic/NRIC n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER a/ADDRESS d/DRUG_ALLERGIES -
register ic/S1234567A n/Ling Zhi Yu p/91234567 a/6 College Avenue East, #00-00, University Town, National University of Singapore, 138614 d/nil
help
-
help -
help
sort
-
sort SORT_TYPE SORT_ORDER -
sort a 123
view
-
view VIEW_NAME -
view default
viewvisitors
-
viewvisitors ic/PATIENT_NRIC -
viewvisitors ic/S1234567A
visitorin
-
visitorin ic/PATIENT_NRIC v/VISITOR_NAME -
visitorin ic/S1234567A v/Sara Ann Nicholas
visitorout
-
visitorout ic/PATIENT_NRIC v/VISITOR_NAME -
visitorout ic/S1234567A v/Sara Ann Nicholas